As derived in the previous section, the moment of inertia
tensor, in 3D Cartesian coordinates, is a three-by-three matrix
![]() that can be multiplied by any angular-velocity vector to
produce the corresponding angular momentum vector for either a point
mass or a rigid mass distribution. Note that the origin of the
angular-velocity vector
that can be multiplied by any angular-velocity vector to
produce the corresponding angular momentum vector for either a point
mass or a rigid mass distribution. Note that the origin of the
angular-velocity vector
![]() is always fixed at
is always fixed at
![]() in the space
(typically located at the center of mass). Therefore, the moment of
inertia tensor
in the space
(typically located at the center of mass). Therefore, the moment of
inertia tensor
![]() is defined relative to that origin.
is defined relative to that origin.
The moment of inertia tensor can similarly be used to compute the
mass moment of inertia for any normalized angular velocity
vector
![]() as
as
![\begin{eqnarray*}
I &=& m \left\Vert\,\underline{x}-(\underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\underline{x})\underline{\tilde{\omega}}\,\right\Vert^2\\ [5pt]
&=& m \left[\underline{x}^T-(\underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\underline{x})\underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\right]
\left[\underline{x}-(\underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\underline{x})\underline{\tilde{\omega}}\right]\\ [5pt]
&=& m \left[\underline{x}^T\underline{x}- \underline{x}^T(\underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\underline{x})\underline{\tilde{\omega}}-(\underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\underline{x})\underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\underline{x}
+(\underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\underline{x})^2\underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\underline{\tilde{\omega}}\right]\\ [5pt]
&=& m \left[\underline{x}^T\underline{x}- (\underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\underline{x})^2\right]
\eqsp
m \left[\left\Vert\,x\,\right\Vert^2 - \underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\underline{x}\underline{x}^T\underline{\tilde{\omega}}\right]\\ [5pt]
&\eqsp & \underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T \left[m \left(\left\Vert\,\underline{x}\,\right\Vert^2\mathbf{E}-\underline{x}\underline{x}^T\right)\right]\underline{\tilde{\omega}}\\ [5pt]
&\isdef & \underline{\tilde{\omega}}^T\mathbf{I}\,\underline{\tilde{\omega}}
\end{eqnarray*}](img2888.png)
where again
![]() denotes the three-by-three identity matrix, and
denotes the three-by-three identity matrix, and
For a collection of ![]() masses
masses ![]() located at
located at
![]() , we
simply sum over their masses to add up the moments of inertia:
, we
simply sum over their masses to add up the moments of inertia:
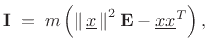
Finally, for a continuous mass distribution, we integrate as usual:
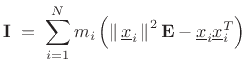
where