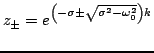Next: Problems
Up: Loss
Previous: Numerical Decay Time
Contents
Index
Just as in the case of the SHO, an exact two-step numerical solution is available in the case of the SHO with loss. Considering the recursion
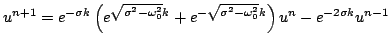 |
(3.92) |
the characteristic polynomial is
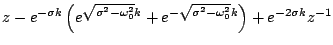 |
(3.93) |
which has roots
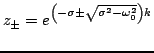 |
(3.94) |
The proof that the difference scheme (3.92) solves the loss SHO exactly may be carried out through the same series expansion methods used in §3.3.4. It is also possible to make a correspondence between scheme (3.92) and a parameterized finite difference scheme--see Problem 3.9
Stefan Bilbao
2006-11-15