Theorem: Let
Theorem: Let ![]() denote a signal with Fourier transform
denote a signal with Fourier transform ![]() , and let
, and let
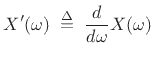 |
(B.6) |
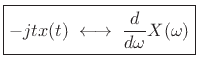 |
(B.7) |
Proof:
We can show this by direct differentiation of the definition of the
Fourier transform:
![\begin{eqnarray*}
X^\prime(\omega) &\isdef & \frac{d}{d\omega} \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) e^{-j\omega t} dt\\
&=& \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) (-jt) e^{-j\omega t} dt\\
&=& \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} [-jtx(t)] e^{-j\omega t} dt\\
&=& \hbox{\sc FT}_\omega\{[-jtx(t)]\}
\end{eqnarray*}](img2420.png)
An alternate method of proof is given in §2.3.13.
The transform-pair may be alternately stated as follows:
 |
(B.8) |