For this example, we have an external force ![]() driving a spring
driving a spring
![]() which is terminated on the other end at a rigid wall.
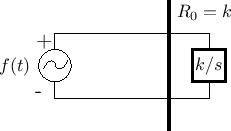
Figure F.18 shows the physical diagram
and the electrical equivalent circuit is given in
Fig.F.19.
which is terminated on the other end at a rigid wall.
Figure F.18 shows the physical diagram
and the electrical equivalent circuit is given in
Fig.F.19.
Figure F.20 depicts the insertion of an infinitesimal transmission line, and Fig.F.21 shows the result of converting the spring impedance to wave variable form.
 |
The two-port adaptor needed for this problem is the same as that for the force-driven mass, and the final result is shown in Fig.F.22.
Note that the spring model is being driven by a force from a zero source impedance, in contrast with the infinite source impedance interpretation of Fig.F.10b as a compressed spring. In this case, if the driving force goes to zero, the spring force goes immediately to zero (``free termination'') rather than remaining fixed.