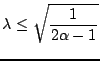Next: A Compact Implicit Scheme
Up: Other Schemes
Previous: Other Schemes
Contents
Index
A Stencil-width Five Scheme
A simple explicit generalization of scheme (6.33) involves a wider-stencil centered approximation to the spatial derivative term:
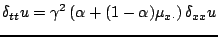 |
(6.60) |
This scheme involves a free parameter 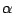 , and reduces to scheme (6.33) when
, and reduces to scheme (6.33) when
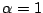 ; it is nominally second-order accurate in both space and time. The form above may be expanded into the following recursion:
; it is nominally second-order accurate in both space and time. The form above may be expanded into the following recursion:
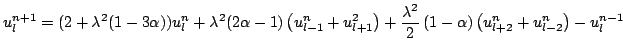 |
(6.61) |
This scheme clearly makes use of points two grid spacings removed from the update point, and thus has a stencil width of five. See Figure ![[*]](file:/usr/share/latex2html/icons/crossref.png) (a) for a representation of the ``footprint" corresponding to this scheme.
(a) for a representation of the ``footprint" corresponding to this scheme.
The characteristic equation for scheme (6.60) is easily obtained, again through the insertion of a test solution of the form
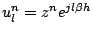 :
:
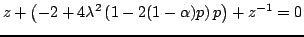 |
(6.62) |
where the short-hand notation
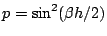 has been used. The condition that the roots of the characteristic equation are of unit magnitude is that
has been used. The condition that the roots of the characteristic equation are of unit magnitude is that
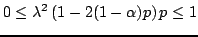 |
(6.63) |
for all values of
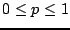 . The left-hand inequality is satisfied for
. The left-hand inequality is satisfied for
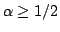 |
(6.64) |
Given the above restriction on 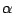 , the right hand inequality yields a bound on
, the right hand inequality yields a bound on 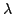 :
:
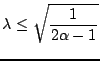 |
(6.65) |
Notice that as 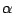 increases,
increases, 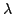 is forced to decrease.
is forced to decrease.





Next: A Compact Implicit Scheme
Up: Other Schemes
Previous: Other Schemes
Contents
Index
Stefan Bilbao
2006-11-15
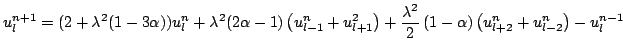
![]() :
: