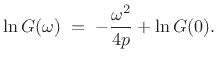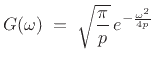Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
The Fourier transform of a complex Gaussian can also be derived using the
differentiation theorem and its dual (§B.2).D.1
Proof: Let
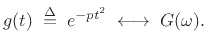 |
(D.19) |
Then by the differentiation theorem (§B.2),
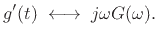 |
(D.20) |
By the differentiation theorem dual (§B.3),
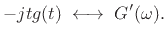 |
(D.21) |
Differentiating 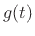 gives
gives
![$\displaystyle g^\prime(t) \eqsp -2ptg(t) \eqsp \frac{2p}{j}[-jtg(t)] \;\longleftrightarrow\;\frac{2p}{j}G^\prime(\omega).$](img2771.png) |
(D.22) |
Therefore,
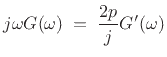 |
(D.23) |
or
![$\displaystyle \left[\ln G(\omega)\right]^\prime \eqsp \frac{G^\prime(\omega)}{G(\omega)} \eqsp -\frac{\omega}{2p} \eqsp \left(-\frac{\omega^2}{4p}\right)^\prime.$](img2773.png) |
(D.24) |
Integrating both sides with respect to 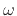 yields
yields
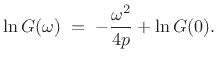 |
(D.25) |
In §D.7, we found that
 , so that, finally,
exponentiating gives
, so that, finally,
exponentiating gives
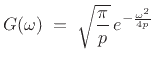 |
(D.26) |
as expected.
The Fourier transform of complex Gaussians (``chirplets'') is used in
§10.6 to analyze Gaussian-windowed ``chirps'' in the
frequency domain.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
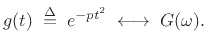
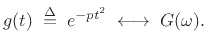
![$\displaystyle g^\prime(t) \eqsp -2ptg(t) \eqsp \frac{2p}{j}[-jtg(t)] \;\longleftrightarrow\;\frac{2p}{j}G^\prime(\omega).$](img2771.png)
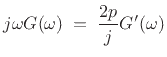
![$\displaystyle \left[\ln G(\omega)\right]^\prime \eqsp \frac{G^\prime(\omega)}{G(\omega)} \eqsp -\frac{\omega}{2p} \eqsp \left(-\frac{\omega^2}{4p}\right)^\prime.$](img2773.png)