Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
A second-order Hadamard matrix may be defined by
with higher order Hadamard matrices defined by recursive embedding, e.g.,
When 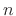 is a power of
is a power of 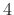 , the Hadamard matrix
, the Hadamard matrix
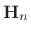 of that
order requires no multiplies in fixed-point arithmetic. An
of that
order requires no multiplies in fixed-point arithmetic. An 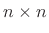 Hadamard matrix has the maximum possible determinant of any
Hadamard matrix has the maximum possible determinant of any
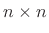 complex matrix containing elements which are bounded by
complex matrix containing elements which are bounded by
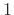 in magnitude. This can be seen as an optimal mixing and
scattering property of the matrix.
in magnitude. This can be seen as an optimal mixing and
scattering property of the matrix.
As of version 0.9.30, Faust's math.lib4.12contains a function called hadamard(n) for generating an
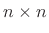 Hadamard matrix, where
Hadamard matrix, where 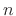 must be a power of
must be a power of 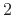 . A
Hadamard feedback matrix is used in the programming example
reverb_designer.dsp (a configurable FDN reverberator)
distributed with Faust.
. A
Hadamard feedback matrix is used in the programming example
reverb_designer.dsp (a configurable FDN reverberator)
distributed with Faust.
A Hadamard feedback matrix is said to be used in the IRCAM
Spatialisateur [219].
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![$\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_2 \isdef
\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}
\left[\begin{array}{rr}
1 & 1\\
1 & -1
\end{array}\right],
$](img747.png)
![$\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_2 \isdef
\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}
\left[\begin{array}{rr}
1 & 1\\
1 & -1
\end{array}\right],
$](img747.png)
![$\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_4 \isdef
\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}
\left[\begin{array}{rr}
\mathbf{H}_2 & \mathbf{H}_2\\
\mathbf{H}_2 & -\mathbf{H}_2
\end{array}\right].
=
\frac{1}{2}
\left[\begin{array}{rrrr}
1& 1& 1& 1\\
1&-1& 1&-1\\
1& 1&-1&-1\\
1&-1&-1& 1
\end{array}\right].
$](img748.png)
![]() Hadamard matrix, where
Hadamard matrix, where ![]() must be a power of
must be a power of ![]() . A
Hadamard feedback matrix is used in the programming example
reverb_designer.dsp (a configurable FDN reverberator)
distributed with Faust.
. A
Hadamard feedback matrix is used in the programming example
reverb_designer.dsp (a configurable FDN reverberator)
distributed with Faust.