The dual of the Poisson Summation Formula is the continuous-time
aliasing theorem, which lies at the foundation of elementary
sampling theory [264, Appendix G]. If ![]() denotes a
continuous-time signal, its sampled version
denotes a
continuous-time signal, its sampled version ![]() ,
,
![]() , is
associated with the continuous-time signal
, is
associated with the continuous-time signal
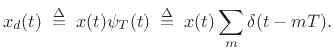 |
(B.60) |
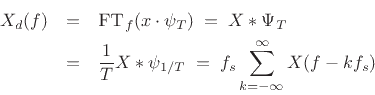
where
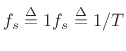 denotes the sampling rate
in radians per second. Note that
denotes the sampling rate
in radians per second. Note that ![]() is periodic
with period
is periodic
with period ![]() . We see that if
. We see that if ![]() is bandlimited to
less than
is bandlimited to
less than ![]() radians per second, i.e., if
radians per second, i.e., if ![]() for all
for all
![]() , then only the
, then only the ![]() term will be
nonzero in the summation over
term will be
nonzero in the summation over ![]() , and this means there is no
aliasing. The terms
, and this means there is no
aliasing. The terms ![]() for
for ![]() are all
aliasing terms.
are all
aliasing terms.