![\begin{eqnarray*}
x(n) &\mathrel{\stackrel{\Delta}{=}}& \frac{1}{N} \sum_{k=0}^{N-1}e^{j\omega_kn} =
\left\{
\begin{array}{ll}
1 & n=0 \quad (\hbox{\sc mod}\ N) \\
0 & \mbox{elsewhere} \\
\end{array} \right. \\ [5pt]
&=& \hbox{\sc IDFT}_n(1 \cdots 1)
\end{eqnarray*}](img1446.png)
Consider the summation of N complex sinusoids having frequencies uniformly spaced around the unit circle [264]:
![\begin{eqnarray*}
x(n) &\mathrel{\stackrel{\Delta}{=}}& \frac{1}{N} \sum_{k=0}^{N-1}e^{j\omega_kn} =
\left\{
\begin{array}{ll}
1 & n=0 \quad (\hbox{\sc mod}\ N) \\
0 & \mbox{elsewhere} \\
\end{array} \right. \\ [5pt]
&=& \hbox{\sc IDFT}_n(1 \cdots 1)
\end{eqnarray*}](img1446.png)
where
 .
.
Setting ![]() (the FFT hop size) gives
(the FFT hop size) gives
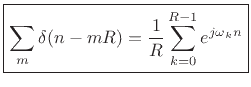 |
(9.26) |
 (harmonics of the frame rate).
(harmonics of the frame rate).
Let us now consider these equivalent signals as inputs to an LTI
system, with an impulse response given by ![]() , and frequency response
equal to
, and frequency response
equal to ![]() .
.
Looking across the top of Fig.8.16, for the case of input signal
![]() we have
we have
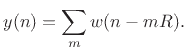 |
(9.27) |
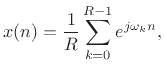 |
(9.28) |
 |
(9.29) |
Since the inputs were equal, the corresponding outputs must be equal too. This derives the Poisson Summation Formula (PSF):
The continuous-time PSF is derived in §B.15.