Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Spectral peak measurement was discussed in Chapter 5.
Given a set of peak frequencies  ,
,
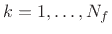 , it is usually
straightforward to form a fundamental frequency estimate
``
, it is usually
straightforward to form a fundamental frequency estimate
`` ''. This task is also called pitch detection, where the
perceived ``pitch'' of the audio signal is assumed to coincide well
enough with its fundamental frequency. We assume here that the signal
is periodic, so that all of its sinusoidal components are
harmonics of a fundamental component having frequency
''. This task is also called pitch detection, where the
perceived ``pitch'' of the audio signal is assumed to coincide well
enough with its fundamental frequency. We assume here that the signal
is periodic, so that all of its sinusoidal components are
harmonics of a fundamental component having frequency  .
(For inharmonic sounds, the perceived pitch, if any, can be complex to
predict [54].)
.
(For inharmonic sounds, the perceived pitch, if any, can be complex to
predict [54].)
An approximate maximum-likelihood  -detection
algorithm11.1 consists
of the following steps:
-detection
algorithm11.1 consists
of the following steps:
- Find the peak of the histogram of the
peak-frequency-differences in order to find the most common harmonic
spacing. This is the nominal
 estimate. The matlab
hist function can be used to form a histogram from the
measured peak-spacings.
estimate. The matlab
hist function can be used to form a histogram from the
measured peak-spacings.
- Refine the nominal
 estimate using linear
regression. A linear regression is a least-squares straight-line fit.
Our straight line is
estimate using linear
regression. A linear regression is a least-squares straight-line fit.
Our straight line is
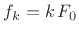 ,
,
 , where
, where  are
the measured harmonic peak frequencies. (The histogram estimate can
be used to reject peaks too far from the expected harmonic frequencies.)
Thus,
are
the measured harmonic peak frequencies. (The histogram estimate can
be used to reject peaks too far from the expected harmonic frequencies.)
Thus,  is the slope of the fitted line.
In matlab, the function
polyfit(x,y,1) can be used. As an ideal example,
p = polyfit([1,2,3],[440,2*440,3*440],1)
returns p = [440,0], where
p(1) is the slope, and p(2) is the offset.
is the slope of the fitted line.
In matlab, the function
polyfit(x,y,1) can be used. As an ideal example,
p = polyfit([1,2,3],[440,2*440,3*440],1)
returns p = [440,0], where
p(1) is the slope, and p(2) is the offset.
A matlab listing for  estimation along these lines appears in §F.6.
estimation along these lines appears in §F.6.
Subsections
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() ,
,
![]() , it is usually
straightforward to form a fundamental frequency estimate
``
, it is usually
straightforward to form a fundamental frequency estimate
``![]() ''. This task is also called pitch detection, where the
perceived ``pitch'' of the audio signal is assumed to coincide well
enough with its fundamental frequency. We assume here that the signal
is periodic, so that all of its sinusoidal components are
harmonics of a fundamental component having frequency
''. This task is also called pitch detection, where the
perceived ``pitch'' of the audio signal is assumed to coincide well
enough with its fundamental frequency. We assume here that the signal
is periodic, so that all of its sinusoidal components are
harmonics of a fundamental component having frequency ![]() .
(For inharmonic sounds, the perceived pitch, if any, can be complex to
predict [54].)
.
(For inharmonic sounds, the perceived pitch, if any, can be complex to
predict [54].)
![]() -detection
algorithm11.1 consists
of the following steps:
-detection
algorithm11.1 consists
of the following steps: