Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
The speed of sound in a gas depends primarily on the
temperature, and can be estimated using the following formula
from the kinetic theory of gases:
E.12
where adiabatic gas constant is
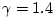 for air at standard
temperature and pressure (STP) (standard temperature is zero degrees
centigrade),
for air at standard
temperature and pressure (STP) (standard temperature is zero degrees
centigrade), 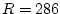 is the ideal gas constant for air (in
meters-squared per second-squared per degrees-Kelvin-squared), and
is the ideal gas constant for air (in
meters-squared per second-squared per degrees-Kelvin-squared), and 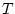 is absolute temperature in degrees Kelvin (which equals degrees
centigrade + 273.15). For example, at zero degrees centigrade (32
degrees Farenheit), the speed of sound is calculated to be 1085.1 feet
per second. At 20 degrees centigrade, we get 1124.1 feet per second.
is absolute temperature in degrees Kelvin (which equals degrees
centigrade + 273.15). For example, at zero degrees centigrade (32
degrees Farenheit), the speed of sound is calculated to be 1085.1 feet
per second. At 20 degrees centigrade, we get 1124.1 feet per second.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite and copy this work]