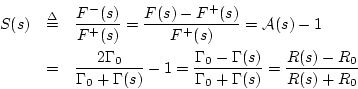Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Calculate the reflectance of the terminated waveguide.
That is, find the Laplace transform of the return wave divided by the
Laplace transform of the input wave going into the waveguide. In general,
the reflectance of an impedance step for force waves (voltage waves in
the electrical case) is
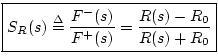 |
(N.1) |
This is easily derived from continuity constraints across the
junction. Specifically, referring to Fig. N.1b, let
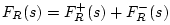 denote the physical force and its traveling-wave
components within the ``pseudo-infinitesimal-generalized-waveguide''
defined by the element impedance
denote the physical force and its traveling-wave
components within the ``pseudo-infinitesimal-generalized-waveguide''
defined by the element impedance 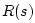 , with the `
, with the `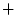 ' superscript
denoting a right-going wave.N.1 Similarly, let
' superscript
denoting a right-going wave.N.1 Similarly, let
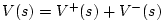 denote the velocity and its component wave variables on
the side of the junction at impedance
denote the velocity and its component wave variables on
the side of the junction at impedance 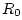 , and let
, and let
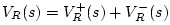 denote the corresponding quantities on the
element-side of the junction at impedance
denote the corresponding quantities on the
element-side of the junction at impedance 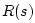 . Again, the `
. Again, the `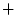 '
superscript denotes travel to the right. Then the physical continuity
constraints imply
'
superscript denotes travel to the right. Then the physical continuity
constraints imply
By the definition of wave impedance in a waveguide, we have
Thus,
Defining
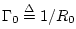 and
and
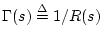 , we have
, we have
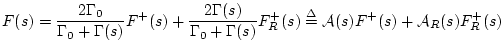 |
(N.2) |
Now that we've solved for the junction force 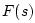 , the outgoing
waves are simply obtained from the force continuity constraint,
, the outgoing
waves are simply obtained from the force continuity constraint,
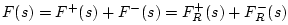 :
:
Finally, the force-wave reflectance of an impedance step from  to
to
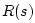 can be found by solving Eq. (N.3) and (N.2) for
can be found by solving Eq. (N.3) and (N.2) for
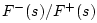 with
with
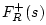 set to zero:
set to zero:
as claimed.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite and copy this work]
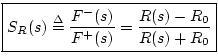
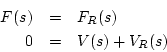
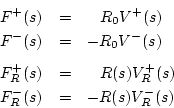
![\begin{eqnarray*}
0 &=& V(s) + V_R(s)\\
&=& \left[V^{+}(s)+V^{-}(s)\right] + ...
...s)}\right]
&=& \frac{2}{R_0}F^{+}(s) + \frac{2}{R(s)}F^{+}_R(s)
\end{eqnarray*}](img3163.png)
![]() and
and
![]() , we have
, we have