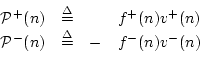 |
Basic courses in physics teach us that power is work per unit time, and work is a measure of energy which is typically defined as force times distance. Therefore, power is in physical units of force times distance per unit time, or force times velocity. It therefore should come as no surprise that traveling power waves are defined for strings as
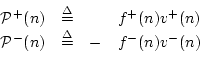 |
| (G.49) |
Power waves are important because they correspond to the actual ability of the wave to do work on the outside world, such as on a violin bridge at the end of a string. Because energy is conserved in closed systems, power waves sometimes give a simpler, more fundamental view of wave phenomena, such as in conical acoustic tubes. Also, implementing nonlinear operations such as rounding and saturation in such a way that signal power is not increased, gives suppression of limit cycles and overflow oscillations [408], as discussed in the section on signal scattering.
For example, consider a waveguide having a wave impedance which
increases smoothly to the right. A converging cone provides a
practical example in the acoustic tube realm. Then since the energy
in a traveling wave must be in the wave unless it has been transduced
elsewhere, we expect
![]() to propagate unchanged along the
waveguide. However, since the wave impedance is increasing, it must
be true that force is increasing and velocity is decreasing according
to
to propagate unchanged along the
waveguide. However, since the wave impedance is increasing, it must
be true that force is increasing and velocity is decreasing according
to
![]() . Looking only at force or velocity
might give us the mistaken impression that the wave is getting
stronger (looking at force) or weaker (looking at velocity), when
really it was simply sailing along as a fixed amount of energy. This
is an example of a transformer action in which force is
converted into velocity or vice versa. It is well known that a
conical tube acts as if it's open on both ends even though we can
plainly see that it is closed on one end. A tempting explanation is
that the cone acts as a transformer which exchanges pressure and
velocity between the endpoints of the tube, so that a closed end on
one side is equivalent to an open end on the other. However, this
view is oversimplified because, while spherical pressure waves travel
nondispersively in cones, velocity propagation is dispersive
[25,45].
. Looking only at force or velocity
might give us the mistaken impression that the wave is getting
stronger (looking at force) or weaker (looking at velocity), when
really it was simply sailing along as a fixed amount of energy. This
is an example of a transformer action in which force is
converted into velocity or vice versa. It is well known that a
conical tube acts as if it's open on both ends even though we can
plainly see that it is closed on one end. A tempting explanation is
that the cone acts as a transformer which exchanges pressure and
velocity between the endpoints of the tube, so that a closed end on
one side is equivalent to an open end on the other. However, this
view is oversimplified because, while spherical pressure waves travel
nondispersively in cones, velocity propagation is dispersive
[25,45].