![$\displaystyle \left[\begin{array}{c} V_1^-(s) \\ [2pt] V_2^-(s) \end{array}\right]= \left[\begin{array}{cc} H_{11}(s) & H_{12}(s) \\ [2pt] H_{21}(s) & H_{22}(s) \end{array}\right] \left[\begin{array}{c} V_1^+(s) \\ [2pt] V_2^+(s) \end{array}\right]. \protect$](img4070.png) |
(C.136) |
In §6.12.2, general coupling of horizontal and vertical planes of vibration in an ideal string was considered. This eigenanalysis will now be applied here to obtain formulas for the damping and mode tuning caused by the coupling of two identical strings at a bridge. This is the case that arises in pianos [547].
The general formula for linear, time-invariant coupling of two strings can be written, in the frequency domain, as
![$\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_c(s) = \left[\begin{array}{cc} 1-H_b(s) & -H_b(s) \\ [2pt] -H_b(s) & 1-H_b(s) \end{array}\right]
$](img4072.png)
where
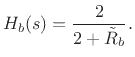
Here
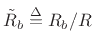 is the bridge impedance divided by the string
impedance. Treating
is the bridge impedance divided by the string
impedance. Treating
![$\displaystyle \underline{e}_1 = \left[\begin{array}{c} 1 \\ [2pt] 1 \end{array}\right],
\qquad
\underline{e}_2 = \left[\begin{array}{c} 1 \\ [2pt] -1 \end{array}\right],
$](img4076.png)
respectively, and the eigenvalues are
Note that only one eigenvalue depends on
We conclude that ``in-phase vibrations'' see a longer effective string length, lengthened by the phase delay of
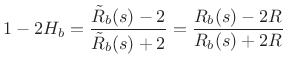
which is the reflectance seen from two in-phase strings each having impedance
We similarly conclude that the ``anti-phase vibrations'' see no length correction at all, because the bridge point does not move at all in this case. In other words, any bridge termination at a point is rigid with respect to anti-phase vibration of the two strings connected to that point.
The above analysis predicts that, in ``stiffness controlled'' frequency intervals (in which the bridge ``looks like a damped spring''), the ``initial fast decay'' of a piano note should be measurably flatter than the ``aftersound,'' while the aftersound should be in tune as if the termination were rigid.