Starting with a dashpot with coefficient ![]() , we have
, we have
and reflectance
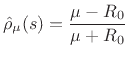
This time, choosing
Conformally mapping the zero function yields the zero function so that
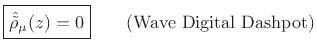
as well. Thus, the WDF of a dashpot is a ``wave sink,'' as diagrammed in Fig.F.4.
In the context of waveguide theory, a zero reflectance corresponds to a matched impedance, i.e., the terminating transmission-line impedance equals the characteristic impedance of the line.
The difference equation for the wave digital dashpot is simply
![]() . While this may appear overly degenerate at first,
remember that the interface to the element is a port at impedance
. While this may appear overly degenerate at first,
remember that the interface to the element is a port at impedance
![]() . Thus, in this particular case only, the infinitesimal
waveguide interface is the element itself.
. Thus, in this particular case only, the infinitesimal
waveguide interface is the element itself.