Physically, the reflection coefficient seen at port ![]() is due to an
impedance step from
is due to an
impedance step from ![]() , that of the port interface, to a new
impedance consisting of the parallel combination of all other
port impedances meeting at the junction. Let
, that of the port interface, to a new
impedance consisting of the parallel combination of all other
port impedances meeting at the junction. Let
Let's check this ``physical'' derivation against the formal definition
Eq.(F.17) leading to
![]() in Eq.(F.19).
Toward this goal, let
in Eq.(F.19).
Toward this goal, let
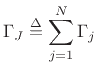
denote the parallel combination of all admittances connected to the junction. Then by Eq.(F.21), we have
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\rho_i &\isdef & \alpha_i - 1
\;\isdef \; \frac{2\Gamma _i}{\Gamma _J} - 1\\
&\isdef & \frac{2\Gamma _i - \Gamma _J}{\Gamma _J}
\;=\; \frac{2\Gamma _i - \left[\Gamma _i + \Gamma _J(i)\right]}{\Gamma _i + \Gamma _J(i)}\\
&=& \frac{\Gamma _i - \Gamma _J(i)}{\Gamma _i + \Gamma _J(i)}
\;=\; \frac{R_J(i) - R_i}{R_J(i)-R_i}
\end{eqnarray*}](img4916.png)
and the result is verified.