As a familiar special case, set
where
The inverse of this polyphase matrix is then simply the inverse DFT matrix:
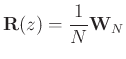
We see that the STFT can be seen as the simple special case of a
perfect reconstruction filter bank for which the polyphase matrix is
constant. It is also unitary when
![]() and
and
![]() .
.
The channel analysis and synthesis filters are, respectively,
![\begin{eqnarray*}
H_k(z) &=& H_0(zW_N^k)\\ [0.1in]
F_k(z) &=& F_0(zW_N^{-k})
\end{eqnarray*}](img281.png)
where
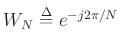 , as usual, and
, as usual, and
![$\displaystyle F_0(z)=H_0(z)=\sum_{n=0}^{N-1}z^{-n}\leftrightarrow[1,1,\ldots,1]
$](img283.png)
corresponding to the rectangular window.
Looking again at the polyphase representation of the ![]() -channel
filter bank with hop size
-channel
filter bank with hop size ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() dividing
dividing ![]() , we have
, we have
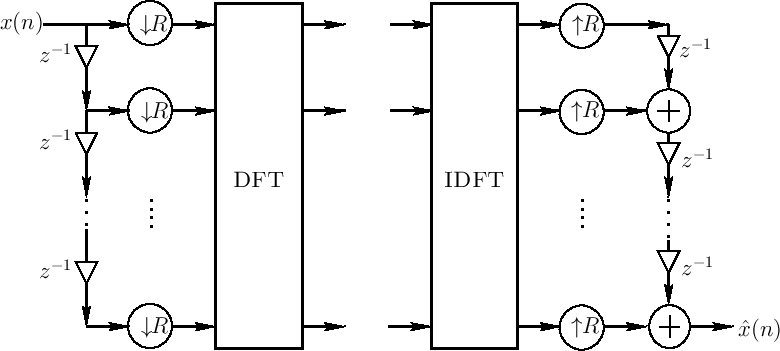
Thus,