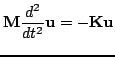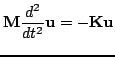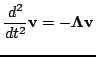Next: A Simple Scheme
Up: The Simple Harmonic Oscillator
Previous: As First-Order System
Contents
Index
Coupled second order ODE systems appear frequently in finite element analysis, and, in musical sound synthesis, directly as descriptions of the dynamics of lumped networks, as described in §1.2.1; what remains, after spatial discretization of an LTI distributed system, is a system of the form:
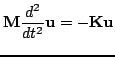 |
(3.16) |
where here, 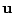 is an
is an 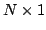 column vector, and
column vector, and 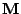 and
and 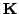 are known as, respectively, the
are known as, respectively, the 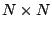 mass and stiffness matrices, which are constants. If the product
mass and stiffness matrices, which are constants. If the product
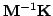 exists and is diagonalizable, with
exists and is diagonalizable, with
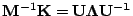 , then the system may be immediately decoupled as
, then the system may be immediately decoupled as
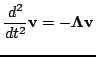 |
(3.17) |
where
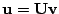 , and
, and
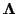 is the diagonal matrix containing the eigenvalues of
is the diagonal matrix containing the eigenvalues of
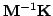 . In most cases of interest,
. In most cases of interest,
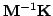 will be symmetric and positive definite.
will be symmetric and positive definite.
Lumped network approaches to sound synthesis, mentioned in §1.2.1, are built, essentially, around such coupled oscillator systems. Some simple examples will appear later in §3.4.





Next: A Simple Scheme
Up: The Simple Harmonic Oscillator
Previous: As First-Order System
Contents
Index
Stefan Bilbao
2006-11-15