Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Definition:
![$\displaystyle w_H(n) = w_R(n) \left[ \alpha + 2 \beta \cos \left( \Omega_M n \right) \right], \quad n \in \mathbb{Z}, \; \Omega_M \isdef \frac{2 \pi}{M}$](img383.png) |
(4.20) |
where
![$\displaystyle w_R(n) \isdefs \left\{\begin{array}{ll} 1, & \left\vert n\right\vert\leq\frac{M-1}{2} \\ [5pt] 0, & \hbox{otherwise} \\ \end{array} \right.$](img384.png) |
(4.21) |
Transform:
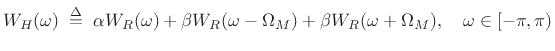 |
(4.22) |
where
 |
(4.23) |
Common Properties
- Rectangular + scaled-cosine window
- Cosine has one period across the window
- Symmetric (
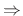 zero or linear phase)
zero or linear phase)
- Positive (by convention on
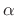 and
and 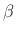 )
)
- Main lobe is
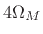 radians per sample wide, where
radians per sample wide, where
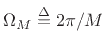
- Zero-crossings (``notches'') in window transform at intervals
of
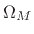 outside of main lobe
outside of main lobe
Figure 3.12 compares the window transforms for the
rectangular, Hann, and Hamming windows. Note how the Hann window has
the fastest roll-off while the Hamming window is closest to being
equal-ripple. The rectangular window has the narrowest main lobe.
Figure 3.12:
Comparison of window
transforms for the rectangular, Hann, and Hamming windows.
![\includegraphics[width=\twidth]{eps/RectHannHamm}](img389.png) |
Rectangular window properties:
- Abrupt transition from 1 to 0 at the window endpoints
- Roll-off is asymptotically
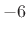 dB per octave (as
dB per octave (as
 )
)
- First side lobe is
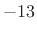 dB relative to main-lobe peak
dB relative to main-lobe peak
Hann window properties:
- Smooth transition to zero at window endpoints
- Roll-off is asymptotically -18 dB per octave
- First side lobe is
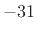 dB relative to main-lobe peak
dB relative to main-lobe peak
Hamming window properties:
- Discontinuous ``slam to zero'' at endpoints
- Roll-off is asymptotically -6 dB per octave
- Side lobes are closer to ``equal ripple''
- First side lobe is
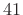 dB down =
dB down = 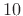 dB better than
Hann4.7
dB better than
Hann4.7
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![$\displaystyle w_H(n) = w_R(n) \left[ \alpha + 2 \beta \cos \left( \Omega_M n \right) \right], \quad n \in \mathbb{Z}, \; \Omega_M \isdef \frac{2 \pi}{M}$](img383.png)
![$\displaystyle w_H(n) = w_R(n) \left[ \alpha + 2 \beta \cos \left( \Omega_M n \right) \right], \quad n \in \mathbb{Z}, \; \Omega_M \isdef \frac{2 \pi}{M}$](img383.png)
![$\displaystyle w_R(n) \isdefs \left\{\begin{array}{ll} 1, & \left\vert n\right\vert\leq\frac{M-1}{2} \\ [5pt] 0, & \hbox{otherwise} \\ \end{array} \right.$](img384.png)