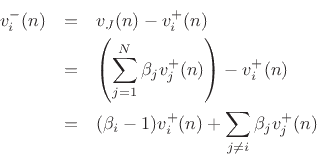Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
The velocity reflection coefficient seen at port
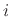 is defined as
is defined as
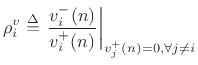 |
(F.38) |
Representing the outgoing velocity wave
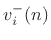 as the
superposition of the reflected wave
as the
superposition of the reflected wave
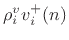 plus the
plus the 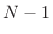 transmitted waves from the other ports, we have
transmitted waves from the other ports, we have
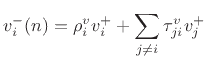 |
(F.39) |
where
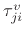 denotes the velocity transmission
coefficient from
port
denotes the velocity transmission
coefficient from
port 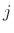 to port
to port 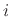 . Substituting Eq.(F.36) into
Eq.(F.37) yields
. Substituting Eq.(F.36) into
Eq.(F.37) yields
Equating like terms with Eq.(F.39) gives
Thus, the 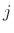 th beta parameter is the velocity transmission
coefficient from
th beta parameter is the velocity transmission
coefficient from 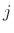 th port to any other port (besides the
th port to any other port (besides the 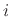 th). To
convert the transmission coefficient from the
th). To
convert the transmission coefficient from the 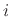 th port to the
reflection coefficient for that port, we simply subtract 1. These
relationships are specific to velocity waves at a series junction
(cf. Eq.(F.19)). They are exactly the dual of Equations (F.19-F.20)
for force waves at a parallel junction.
th port to the
reflection coefficient for that port, we simply subtract 1. These
relationships are specific to velocity waves at a series junction
(cf. Eq.(F.19)). They are exactly the dual of Equations (F.19-F.20)
for force waves at a parallel junction.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() is defined as
is defined as