Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
The reflection coefficient seen at port 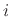 is defined as
is defined as
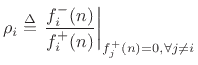 |
(F.17) |
In other words, the reflection coefficient specifies what portion of
the incoming wave
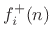 is reflected back to port
is reflected back to port 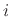 as
part of the outgoing wave
as
part of the outgoing wave
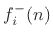 . The total outgoing wave on port
. The total outgoing wave on port
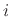 is the superposition of the reflected wave and the
is the superposition of the reflected wave and the 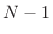 transmitted waves from the other ports:
transmitted waves from the other ports:
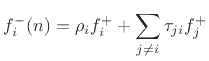 |
(F.18) |
where 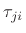 denotes the transmission coefficient from
port
denotes the transmission coefficient from
port 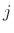 to port
to port 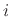 . Starting with Eq.(F.16) and substituting
Eq.(F.15) gives
. Starting with Eq.(F.16) and substituting
Eq.(F.15) gives
Equating like terms with Eq.(F.18), we obtain
Thus, the 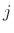 th alpha parameter is the force transmission coefficient
from
th alpha parameter is the force transmission coefficient
from 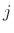 th port to any other port (besides the
th port to any other port (besides the 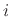 th). To convert the
transmission coefficient from the
th). To convert the
transmission coefficient from the 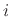 th port to the reflection
coefficient for that port, we simply subtract 1. This general
relationship is specific to force waves at a parallel junction, as we
will soon see.
th port to the reflection
coefficient for that port, we simply subtract 1. This general
relationship is specific to force waves at a parallel junction, as we
will soon see.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() is defined as
is defined as
