Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Power Theorem
The power theorem for Fourier transforms states that the
inner product of two signals in the time domain equals
their inner product in the frequency domain.
The inner product of two spectra 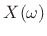 and
and 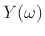 may
be defined as
may
be defined as
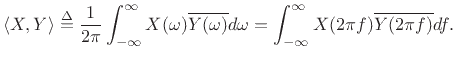 |
(B.21) |
This expression can be interpreted as the inverse Fourier transform of
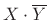 evaluated at
evaluated at  :
:
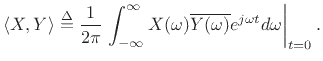 |
(B.22) |
By the convolution theorem (§B.7)
and flip theorem (§B.8),
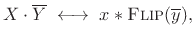 |
(B.23) |
which at 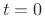 gives
gives
 |
(B.24) |
Thus,
 |
(B.25) |
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() and
and ![]() may
be defined as
may
be defined as