In 1976 [212], Portnoff observed that any window ![]() of the form
of the form
| (10.23) |
sinc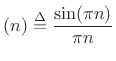 |
(10.24) |
Portnoff suggested that, in practical usage, windowed data segments
longer than the FFT size should be time-aliased about length
![]() prior to performing an FFT. This result is readily derived from the
definition of the time-normalized STFT introduced in Eq.(8.21):
prior to performing an FFT. This result is readily derived from the
definition of the time-normalized STFT introduced in Eq.(8.21):
![\begin{eqnarray*}
{\tilde X}_m(\omega_k)
&\isdef & \hbox{\sc Sample}_{\Omega_N,k}\left(\hbox{\sc DTFT}\left({\tilde x}_m\right)\right) \\
&\isdef & \hbox{\sc Sample}_{\Omega_N,k}\left(\hbox{\sc DTFT}\left(\hbox{\sc Shift}_{-m}(x)\cdot w\right)\right) \\
&=& \sum_{n=-\infty}^\infty x(n+m)w(n)e^{-j\omega_k n}\quad\hbox{(now let $n\isdef lN+i$)}\\
&=& \sum_{l=-\infty}^\infty \sum_{i=0}^{N-1}x(lN+i+m)w(lN+i)
\underbrace{e^{-j\omega_k (lN+i)}}_{e^{-j\omega_k i}}\\
&=& \sum_{i=0}^{N-1}\left[\sum_{l=-\infty}^\infty x(lN+i+m)w(lN+i)\right]
e^{-j\omega_k i}\\
&=& \sum_{i=0}^{N-1}\hbox{\sc Alias}_{N,i}[\hbox{\sc Shift}_{-m}(x)\cdot w] e^{-j\omega_k i}\\
&\isdef & \hbox{\sc DFT}_{N,k}\{\hbox{\sc Alias}_N[\hbox{\sc Shift}_{-m}(x)\cdot w]\},
\end{eqnarray*}](img1645.png)
where
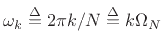 as usual.
as usual.
Choosing ![]() allows multiple side lobes of the sinc function to
alias in on the main lobe. This gives channel filters in the
frequency domain which are sharper bandpass filters while remaining COLA.
I.e., there is less channel cross-talk in the frequency domain.
However, the time-aliasing
corresponds to undersampling in the frequency domain, implying less
robustness to spectral modifications, since such modifications can
disturb the time-domain aliasing cancellation. Since the hop size
needs to be less than
allows multiple side lobes of the sinc function to
alias in on the main lobe. This gives channel filters in the
frequency domain which are sharper bandpass filters while remaining COLA.
I.e., there is less channel cross-talk in the frequency domain.
However, the time-aliasing
corresponds to undersampling in the frequency domain, implying less
robustness to spectral modifications, since such modifications can
disturb the time-domain aliasing cancellation. Since the hop size
needs to be less than ![]() , the overall filter bank based on a Portnoff
window remains oversampled in the time domain.
, the overall filter bank based on a Portnoff
window remains oversampled in the time domain.