Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
In a weighted overlap-add system, the following windows can be used
to satisfy the constant-overlap-add condition:
- For the rectangular window,
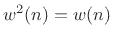 , and
, and
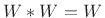 (since
(since
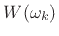 is a sinc function which reduces to
is a sinc function which reduces to
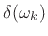 when
when
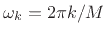 , and
, and
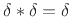 .
.
- For the Hamming window, the critically sampled window transform
has three nonzero samples (where the rectangular-window transform has
one). Therefore,
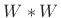 has
has 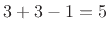 nonzero samples at critical
sampling. Measuring main-lobe width from zero-crossing to
zero-crossing as usual, we get
nonzero samples at critical
sampling. Measuring main-lobe width from zero-crossing to
zero-crossing as usual, we get
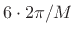 radians per sample, or
``6 side lobes'', for the width of
radians per sample, or
``6 side lobes'', for the width of 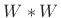 .
.
- The squared-Blackman window transform width is
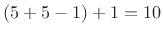 .
.
- The square of a length
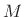
 -term Blackman-Harris-family window
(where rect is
-term Blackman-Harris-family window
(where rect is 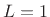 , Hann is
, Hann is 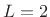 , etc.) has a main lobe of width
, etc.) has a main lobe of width
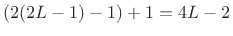 , measured from zero-crossing to zero-crossing in
``side-lobe units'' (
, measured from zero-crossing to zero-crossing in
``side-lobe units'' (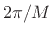 ). This is up from
). This is up from
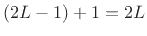 for the
original
for the
original  -term window.
-term window.
- The width of the main lobe can be used to determine the
hop size in the STFT, as will be discussed further in
Chapter 9.
Note that we need only find the first zero-crossing in the
window transform for any member of the Blackman-Harris window family
(Chapter 3), since nulls at all harmonics of
that frequency will always be present (at multiples of 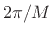 ).
).
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() ).
).