We may define imaginary exponents the same way that all
sufficiently smooth real-valued functions of a real variable are
generalized to the complex case--using Taylor series. A
Taylor series expansion is just a polynomial (possibly of infinitely
high order), and polynomials involve only addition, multiplication,
and division. Since these elementary operations are also defined for
complex numbers, any smooth function of a real variable ![]() may be
generalized to a function of a complex variable
may be
generalized to a function of a complex variable ![]() by simply
substituting the complex variable
by simply
substituting the complex variable ![]() for the real variable
for the real variable ![]() in the Taylor series expansion of
in the Taylor series expansion of ![]() .
.
Let
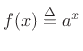 , where
, where ![]() is any positive real number and
is any positive real number and ![]() is
real. The Taylor
series expansion about
is
real. The Taylor
series expansion about ![]() (``Maclaurin series''),
generalized to the complex case is then
(``Maclaurin series''),
generalized to the complex case is then