The two forms of energy in a wave are kinetic and
potential. Denoting them at a particular time ![]() and position
and position
![]() by
by
![]() and
and
![]() , respectively, we can write them in
terms of velocity
, respectively, we can write them in
terms of velocity ![]() and wave impedance
and wave impedance ![]() as follows:
as follows:
![\begin{eqnarray*}
w_v &=& \frac{1}{2} \rho v^2 \eqsp \frac{1}{2c} R v^2 \quad\left(\frac{\mbox{\small Energy}}{\mbox{\small Volume}}\right)\\ [10pt]
w_p &=& \frac{1}{2} \frac{p^2}{\rho c^2} \eqsp \frac{1}{2c} \frac{p^2}{R} \quad\left(\frac{\mbox{\small Energy}}{\mbox{\small Volume}}\right)
\end{eqnarray*}](img3089.png)
More specifically, ![]() and
and ![]() may be called the acoustic kinetic
energy density and the acoustic potential energy density, respectively.
may be called the acoustic kinetic
energy density and the acoustic potential energy density, respectively.
At each point in a plane wave, we have
![]() (pressure equals wave-impedance times velocity), and so
(pressure equals wave-impedance times velocity), and so
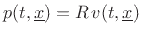
where
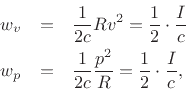 denotes the acoustic
intensity (pressure times velocity) at time
denotes the acoustic
intensity (pressure times velocity) at time ![]() and position
and position
![]() .
Thus, half of the acoustic intensity
.
Thus, half of the acoustic intensity ![]() in a plane wave is kinetic,
and the other half is potential:B.30
in a plane wave is kinetic,
and the other half is potential:B.30
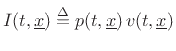
Note that acoustic intensity