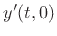When a traveling wave reflects from the bridge of a real stringed
instrument, the bridge moves, transmitting sound energy into the
instrument body. How far the bridge moves is determined by the
driving-point impedance of the bridge, denoted ![]() . The
driving-point impedance is the ratio of the Laplace-transform of the force
on the bridge,
. The
driving-point impedance is the ratio of the Laplace-transform of the force
on the bridge, ![]() , divided by the velocity-of-motion that results,
, divided by the velocity-of-motion that results,
![]() . That is,
. That is,
![]() .
.
For passive systems (i.e., for all unamplified acoustic musical
instruments), the driving-point impedance ![]() is positive
real (a property defined and discussed in §C.11.2). Being
positive real has strong implications on the nature of
is positive
real (a property defined and discussed in §C.11.2). Being
positive real has strong implications on the nature of ![]() . In
particular, the phase of
. In
particular, the phase of
![]() cannot exceed plus or minus
cannot exceed plus or minus
![]() degrees at any frequency, and in the lossless case, all poles and
zeros must interlace along the
degrees at any frequency, and in the lossless case, all poles and
zeros must interlace along the ![]() axis. Another
implication is that the reflectance of a passive bridge, as
seen by traveling waves on the string, is a so-called Schur
function (defined and discussed in §C.11); a Schur
reflectance is a stable filter having gain not exceeding 1 at any
frequency. In summary, a guitar bridge is passive if and only if its
driving-point impedance is positive real and (equivalently) its
reflectance is Schur. See §C.11 for a fuller discussion of
this point.
axis. Another
implication is that the reflectance of a passive bridge, as
seen by traveling waves on the string, is a so-called Schur
function (defined and discussed in §C.11); a Schur
reflectance is a stable filter having gain not exceeding 1 at any
frequency. In summary, a guitar bridge is passive if and only if its
driving-point impedance is positive real and (equivalently) its
reflectance is Schur. See §C.11 for a fuller discussion of
this point.
At ![]() , the force on the bridge is given by (§C.7.2)
, the force on the bridge is given by (§C.7.2)
where
due to linearity, and the velocity of the string endpoint is therefore