Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
In state-space form (§1.3.7) [452],8.7a general class of 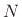 th-order Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE),
can be written as
th-order Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE),
can be written as
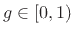 |
(8.9) |
where 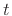 denotes time in seconds,
denotes time in seconds,
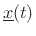 denotes a vector of
denotes a vector of 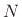 state variables at time
state variables at time 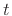 ,
,
denotes the time derivative of
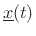 , and
, and
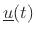 is a vector (any
length) of the system input signals, if any. Thus, Eq.(7.9) says
simply that the time-derivative of the state vector is some function
is a vector (any
length) of the system input signals, if any. Thus, Eq.(7.9) says
simply that the time-derivative of the state vector is some function
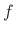 depending on time
depending on time 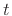 , the current state
, the current state
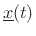 , and the current
input signals
, and the current
input signals
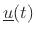 . The basic problem is to solve for the state
trajectory
. The basic problem is to solve for the state
trajectory
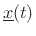 given its initial condition
given its initial condition
 , the system
definition function
, the system
definition function 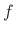 , and the input signals
, and the input signals
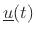 for all
for all 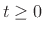 .
.
In the linear, time-invariant (LTI) case, Eq.(7.9) can be
expressed in the usual state-space form for LTI continuous-time
systems:
 |
(8.10) |
In this case, standard methods for converting a filter from continuous
to discrete time may be used, such as the FDA (§7.3.1) and
bilinear transform (§7.3.2).8.8
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() th-order Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE),
can be written as
th-order Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE),
can be written as
