Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Repeat Operator
Like the
 and
and
 operators, the
operators, the
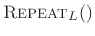 operator maps a length
operator maps a length 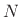 signal to a length
signal to a length
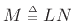 signal:
signal:
Definition: The repeat  times operator is defined for any
times operator is defined for any
 by
by
where
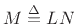 , and indexing of
, and indexing of 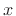 is modulo
is modulo 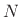 (periodic extension).
Thus, the
(periodic extension).
Thus, the
 operator simply repeats
its input signal
operator simply repeats
its input signal  times.7.11 An example of
times.7.11 An example of
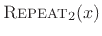 is shown in
Fig.7.8. The example is
is shown in
Fig.7.8. The example is
Figure:
Illustration of
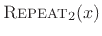 .
.
![\includegraphics[width=\twidth]{eps/repeat}](img1251.png) |
A frequency-domain example is shown in Fig.7.9.
Figure 7.9a shows the original spectrum 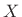 , Fig.7.9b
shows the same spectrum plotted over the unit circle in the
, Fig.7.9b
shows the same spectrum plotted over the unit circle in the 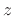 plane,
and Fig.7.9c shows
plane,
and Fig.7.9c shows
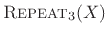 . The
. The  point (dc) is on
the right-rear face of the enclosing box. Note that when viewed as
centered about
point (dc) is on
the right-rear face of the enclosing box. Note that when viewed as
centered about 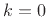 ,
, 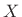 is a somewhat ``triangularly shaped''
spectrum. We see three copies of this shape in
is a somewhat ``triangularly shaped''
spectrum. We see three copies of this shape in
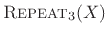 .
.
Figure:
Illustration of
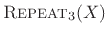 .
a) Conventional plot of
.
a) Conventional plot of 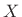 .
b) Plot of
.
b) Plot of 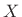 over the unit circle in the
over the unit circle in the 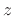 plane.
c)
plane.
c)
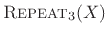 .
.
![\includegraphics[width=4in]{eps/repeat3d}](img1253.png) |
The repeat operator is used to state the Fourier theorem
where
 is defined in §7.2.6. That is, when you
stretch a signal by the factor
is defined in §7.2.6. That is, when you
stretch a signal by the factor  (inserting zeros between the
original samples), its spectrum is repeated
(inserting zeros between the
original samples), its spectrum is repeated  times around the unit
circle. The simple proof is given on page
times around the unit
circle. The simple proof is given on page ![[*]](../icons/crossref.png) .
.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() and
and
![]() operators, the
operators, the
![]() operator maps a length
operator maps a length ![]() signal to a length
signal to a length
![]() signal:
signal:
![]() times operator is defined for any
times operator is defined for any
![]() by
by
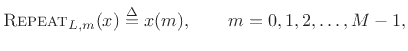
![]() , Fig.7.9b
shows the same spectrum plotted over the unit circle in the
, Fig.7.9b
shows the same spectrum plotted over the unit circle in the ![]() plane,
and Fig.7.9c shows
plane,
and Fig.7.9c shows
![]() . The
. The ![]() point (dc) is on
the right-rear face of the enclosing box. Note that when viewed as
centered about
point (dc) is on
the right-rear face of the enclosing box. Note that when viewed as
centered about ![]() ,
, ![]() is a somewhat ``triangularly shaped''
spectrum. We see three copies of this shape in
is a somewhat ``triangularly shaped''
spectrum. We see three copies of this shape in
![]() .
.
![\includegraphics[width=4in]{eps/repeat3d}](img1253.png)