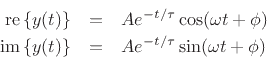We have defined sinusoids and extended the definition to include complex sinusoids. We now extend one more step by allowing for exponential amplitude envelopes:

where
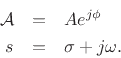
When ![]() , we obtain
, we obtain
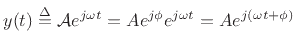
which is the complex sinusoid at amplitude
![\begin{eqnarray*}
y(t) &\isdef & {\cal A}e^{st} \\
&\isdef & A e^{j\phi} e^{(\sigma+j\omega) t} \\
&=& A e^{(\sigma+j\omega) t + j\phi} \\
&=& A e^{\sigma t} e^{j(\omega t + \phi)} \\
&=& A e^{\sigma t} \left[\cos(\omega t + \phi) + j\sin(\omega t + \phi)\right].
\end{eqnarray*}](img594.png)
Defining
![]() , we see that the generalized complex sinusoid
is just the complex sinusoid we had before with an exponential envelope:
, we see that the generalized complex sinusoid
is just the complex sinusoid we had before with an exponential envelope: