
Sound Pressure Level (SPL) is a dB scale defined relative to a reference that is approximately the intensity of a 1000 Hz sinusoid that is just barely audible (zero ``phons''). In pressure units, the reference root-mean-square (rms) amplitude for dB SPL calculation isF.6

The dB SPL reference intensity is given by
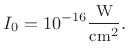
In SI units, this is
Since sound is created by a time-varying pressure, we compute sound levels in dB-SPL by using the average fluctuation-intensity (averaged over at least one period of the lowest frequency contained in the sound).
The wave impedance of air plays the role of ``resistor'' in
relating the pressure- and intensity-based references exactly
analogous to the dBm case discussed above. Using a typical SI value
of ![]() for the acoustic wave impedance (calculatable as the
density of air
for the acoustic wave impedance (calculatable as the
density of air ![]() times the speed of sound
times the speed of sound ![]() ), and the basic
formula
), and the basic
formula
![]() relating intensity to rms pressure, we
calculate
relating intensity to rms pressure, we
calculate
![]() , in agreement with the SI value above for the
rms-pressure-reference for dB SPL.
, in agreement with the SI value above for the
rms-pressure-reference for dB SPL.
Table F.1 gives a list of common sound levels and their dB equivalents [56]. In other references, the ``threshold of pain'' is defined as 120 dB-SPL. Note that hearing damage is a function of both level and duration of exposure.
|
The relationship between sound amplitude and actual loudness is complex [79]. Loudness is a perceptual dimension while sound amplitude is physical. Since loudness sensitivity is closer to logarithmic than linear in amplitude (especially at moderate to high loudnesses), we typically use decibels to represent sound amplitude, especially in spectral displays.
The sone amplitude scale is defined in terms of actual loudness perception experiments [79]. At 1kHz and above, loudness perception is approximately logarithmic above 50 dB SPL or so. Below that, it tends toward being more linear.
The phon amplitude scale is simply the dB scale at 1kHz [79, p. 111]. At other frequencies, the amplitude in phons is defined by following the equal-loudness curve over to 1 kHz and reading off the level there in dB SPL. In other words, all pure tones have the same loudness at the same phon level, and 1 kHz is used to set the reference in dB SPL. Just remember that one phon is one dB-SPL at 1 kHz. Looking at the Fletcher-Munson equal-loudness curves [79, p. 124], loudness in phons can be read off along the vertical line at 1 kHz.
Classically, the intensity level of a sound wave is its dB SPL
level, measuring the peak time-domain pressure-wave amplitude relative to
![]() watts per centimeter squared (i.e., there is no consideration of
the frequency domain here at all).
watts per centimeter squared (i.e., there is no consideration of
the frequency domain here at all).
Another classical term still encountered is the sensation level of pure tones: The sensation level is the number of dB SPL above the hearing threshold at that frequency [79, p. 110].