The polar pattern for a microphone or loudspeaker is its gain
along a circle of constant radius away from the diaphragm/driver. For
a spherical-wave ``point-source'', the polar pattern is simply a
constant at each radius, e.g.,
![]() , where
, where ![]() denotes
the pressure-scaling at
denotes
the pressure-scaling at ![]() and
and ![]() denotes the distance from the
center of the source.
denotes the distance from the
center of the source.
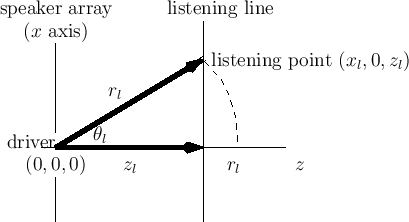
Since our speaker arrays are typically flat, we need to calculate
a slice through the polar pattern along a listening line
(or plane) which we will take to be parallel to the array and to the
![]() axis, as shown in Fig.15. The polar-pattern slice is
then be considered as one sample (interpolation kernel) used to
reconstruct the soundfield at a distance
axis, as shown in Fig.15. The polar-pattern slice is
then be considered as one sample (interpolation kernel) used to
reconstruct the soundfield at a distance ![]() from the array.
from the array.
|
http://arxiv.org/abs/1911.07575.