 |
Figure 6.2 illustrates the parallel combination of two
filters. The filters ![]() and
and ![]() are driven by the
same input signal
are driven by the
same input signal ![]() , and their respective outputs
, and their respective outputs ![]() and
and ![]() are summed. The transfer function of the parallel
combination is therefore
are summed. The transfer function of the parallel
combination is therefore
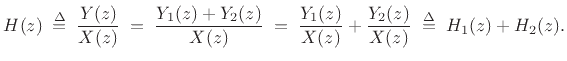
where we needed only linearity of the z transform to have that