We've now defined ![]() for any positive real number
for any positive real number ![]() and any
complex number
and any
complex number ![]() . Setting
. Setting ![]() and
and ![]() gives us the
special case we need for Euler's identity. Since
gives us the
special case we need for Euler's identity. Since ![]() is its own
derivative, the Taylor series expansion for
is its own
derivative, the Taylor series expansion for ![]() is one of
the simplest imaginable infinite series:
is one of
the simplest imaginable infinite series:
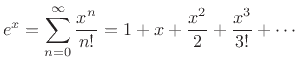
The simplicity comes about because
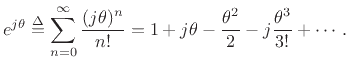
Note that all even-order terms are real while all odd-order terms are imaginary. Separating out the real and imaginary parts gives
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\mbox{re}\left\{e^{j\theta}\right\} &=& 1 - \theta^2/2 + \theta^4/4! - \cdots \\ [5pt]
\mbox{im}\left\{e^{j\theta}\right\} &=& \theta - \theta^3/3! + \theta^5/5! - \cdots\,.
\end{eqnarray*}](img314.png)
Comparing the Maclaurin expansion for
![]() with that of
with that of
![]() and
and
![]() proves Euler's identity. Recall
from introductory calculus that
proves Euler's identity. Recall
from introductory calculus that
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\frac{d}{d\theta}\cos(\theta) &=& -\sin(\theta) \\ [5pt]
\frac{d}{d\theta}\sin(\theta) &=& \cos(\theta)
\end{eqnarray*}](img317.png)
so that
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\left.\frac{d^n}{d\theta^n}\cos(\theta)\right\vert _{\theta=0}
&=& \left\{\begin{array}{ll}
(-1)^{n/2}, & n\;\mbox{\small even} \\ [5pt]
0, & n\;\mbox{\small odd} \\
\end{array} \right. \\ [10pt]
\left.\frac{d^n}{d\theta^n}\sin(\theta)\right\vert _{\theta=0}
&=& \left\{\begin{array}{ll}
(-1)^{(n-1)/2}, & n\;\mbox{\small odd} \\ [5pt]
0, & n\;\mbox{\small even}. \\
\end{array} \right.
\end{eqnarray*}](img318.png)
Plugging into the general Maclaurin series gives
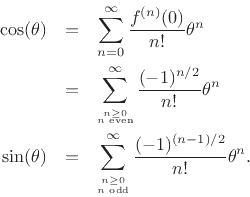
Separating the Maclaurin expansion for
![]() into its even and odd
terms (real and imaginary parts) gives
into its even and odd
terms (real and imaginary parts) gives
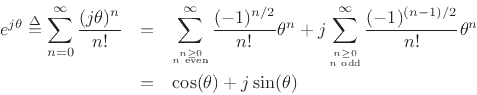
thus proving Euler's identity.