Let the FIR filter length be ![]() samples, with
samples, with ![]() even, and suppose
we'll initially design it to be centered about the time origin
(``zero-phase''). Then the frequency response is given on our
frequency grid
even, and suppose
we'll initially design it to be centered about the time origin
(``zero-phase''). Then the frequency response is given on our
frequency grid ![]() by
by
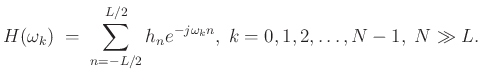
Enforcing even symmetry in the impulse response, i.e.,
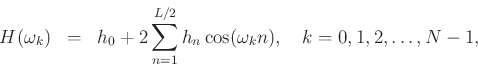
or in matrix form:
![$\displaystyle \left[ \begin{array}{c}
H(\omega_0) \\ H(\omega_1) \\ \vdots \\ H(\omega_{N-1})
\end{array} \right]
=
\underbrace{\left[ \begin{array}{ccccc}
1 & 2\cos(\omega_0) & \dots & 2\cos[\omega_0(L/2)] \\
1 & 2\cos(\omega_1) & \dots & 2\cos[\omega_1(L/2)] \\
\vdots & & & \\
1 & 2\cos(\omega_{N-1}) & \dots & 2\cos[\omega_{N-1}(L/2)]
\end{array} \right]}_A
\underbrace{\left[ \begin{array}{c}
h_0 \\ h_1 \\ \vdots \\ h_{L/2}
\end{array} \right]}_x
$](img159.png)
Note that Remez exchange algorithms are also based on this formulation
internally, but now ![]() .
.