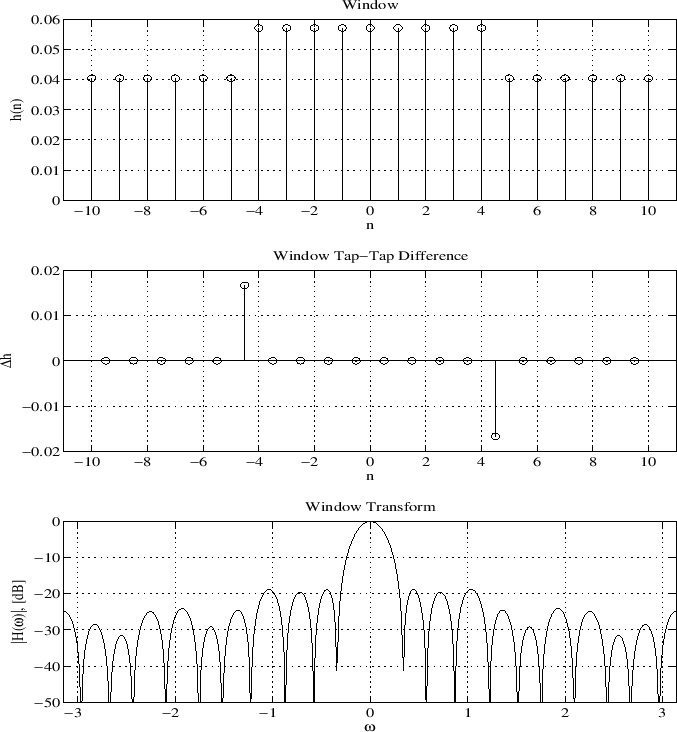
Another way to add a smoothness constraint is to add the ![]() - norm
of the derivative to the objective.
- norm
of the derivative to the objective.
or, in matrix form,
![\begin{displaymath}
\left[\begin{array}{c}
-\mathbf{D}\\
\mathbf{D}\end{array} \right]h
-
\left[
\begin{array}{c}
\underline{\tau} \\
\underline{\tau}
\end{array}\right]\le 0.\end{displaymath}](img71.png)
The objective function becomes
![]() norm of diff(h) added to the objective function (
norm of diff(h) added to the objective function (![]() ):
):
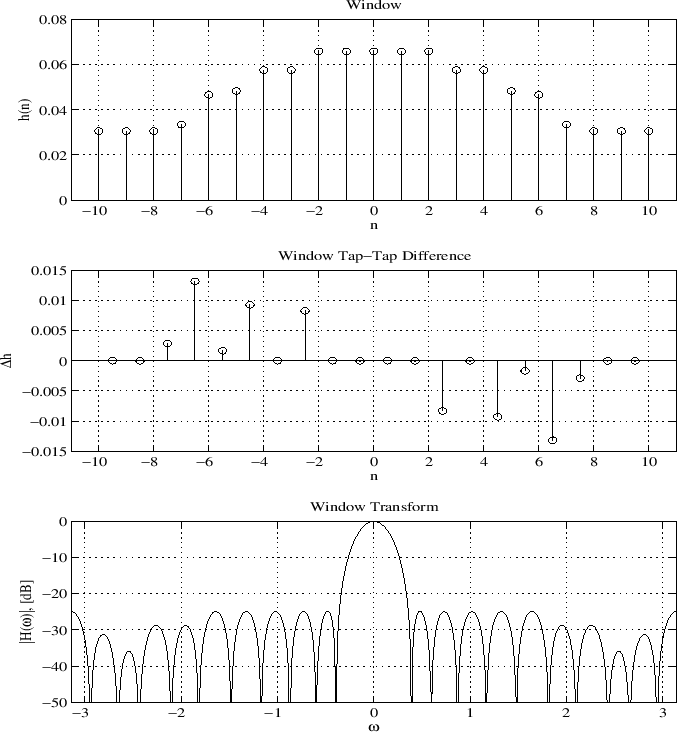
Six times the ![]() norm of diff(h) added to the objective
function (
norm of diff(h) added to the objective
function (![]() ):
):