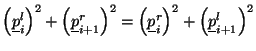Next: Discrete-time Vocal Tract Model
Up: Case Study: The Kelly-Lochbaum
Previous: Junctions Between Two Uniform
At the junction between the 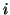 th and
th and 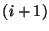 th tubes, the continuity relations (1.5), when multiplied together, imply that
th tubes, the continuity relations (1.5), when multiplied together, imply that
This is simply a statement of conservation of power at the interface. Using the definitions of traveling wave variables from (1.6), we then have that
or, rearranging terms,
In other words, the sum of the squares of the incident waves, weighted by their respective tube admittances, is equal to the same weighted square sum of the reflected waves. Assuming that the 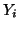 are positive, then, a weighted
are positive, then, a weighted 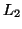 measure of the signal variables (pressure waves) is preserved through the scattering operation. This reflects the inherent losslessness of the tube interface.
measure of the signal variables (pressure waves) is preserved through the scattering operation. This reflects the inherent losslessness of the tube interface.
In terms of the power-normalized variables defined by (1.9), and scattered according to (1.10), we will have (due to the orthogonality of the scattering matrix),
Thus the 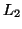 norms of the incident and reflected vectors of power-normalized wave variables are the same.
norms of the incident and reflected vectors of power-normalized wave variables are the same.



Next: Discrete-time Vocal Tract Model
Up: Case Study: The Kelly-Lochbaum
Previous: Junctions Between Two Uniform
Stefan Bilbao
2002-01-22
![]() th and
th and ![]() th tubes, the continuity relations (1.5), when multiplied together, imply that
th tubes, the continuity relations (1.5), when multiplied together, imply that