Next: The Triangular Scheme
Up: The Interpolated Rectilinear Scheme
Previous: The Interpolated Rectilinear Scheme
Although the choice of the free parameter 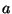 which gives a maximally direction-independent numerical dispersion profile has been made, in the past, through computerized optimization procedures [157], we note here that it is possible to make a theoretical choice as well, based on a Taylor series expansion of the spectrum.
which gives a maximally direction-independent numerical dispersion profile has been made, in the past, through computerized optimization procedures [157], we note here that it is possible to make a theoretical choice as well, based on a Taylor series expansion of the spectrum.
The spectral amplification factors for the interpolated scheme can be written in terms of the function
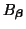 , or, equivalently, in terms of the function
, or, equivalently, in terms of the function
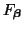 . It should be clear, then, that if
. It should be clear, then, that if
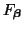 is directionally-independent, then so are the amplification factors, and thus the numerical phase velocity (see §A.1.4) as well. Ideally, we would like
is directionally-independent, then so are the amplification factors, and thus the numerical phase velocity (see §A.1.4) as well. Ideally, we would like
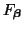 to be a function of the spectral radius
to be a function of the spectral radius

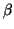
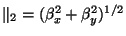 alone. Now examine the Taylor expansion of
alone. Now examine the Taylor expansion of
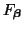 about
about 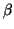
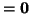 :
:
The directionally-independent
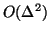 term reflects the fact that the scheme is consistent with the wave equation; higher order terms in general show directional dependence. The choice of
term reflects the fact that the scheme is consistent with the wave equation; higher order terms in general show directional dependence. The choice of 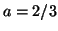 , however, gives
, however, gives
and the directional dependence is confined to higher-order powers of  . Thus for this choice of
. Thus for this choice of 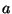 , the numerical scheme is maximally direction independent about spatial DC. Note that this value of
, the numerical scheme is maximally direction independent about spatial DC. Note that this value of 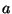 does fall within the required bounds for a passive waveguide mesh implementation. The value of
does fall within the required bounds for a passive waveguide mesh implementation. The value of 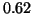 (for which the numerical dispersion profile is plotted in Figure A.2), which is very close to
(for which the numerical dispersion profile is plotted in Figure A.2), which is very close to  , was chosen by visual inspection of dispersion profiles for various values of
, was chosen by visual inspection of dispersion profiles for various values of 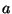 .
.



Next: The Triangular Scheme
Up: The Interpolated Rectilinear Scheme
Previous: The Interpolated Rectilinear Scheme
Stefan Bilbao
2002-01-22
![]() which gives a maximally direction-independent numerical dispersion profile has been made, in the past, through computerized optimization procedures [157], we note here that it is possible to make a theoretical choice as well, based on a Taylor series expansion of the spectrum.
which gives a maximally direction-independent numerical dispersion profile has been made, in the past, through computerized optimization procedures [157], we note here that it is possible to make a theoretical choice as well, based on a Taylor series expansion of the spectrum.
![]() , or, equivalently, in terms of the function
, or, equivalently, in terms of the function
![]() . It should be clear, then, that if
. It should be clear, then, that if
![]() is directionally-independent, then so are the amplification factors, and thus the numerical phase velocity (see §A.1.4) as well. Ideally, we would like
is directionally-independent, then so are the amplification factors, and thus the numerical phase velocity (see §A.1.4) as well. Ideally, we would like
![]() to be a function of the spectral radius
to be a function of the spectral radius
![]()
![]()
![]() alone. Now examine the Taylor expansion of
alone. Now examine the Taylor expansion of
![]() about
about ![]()
![]() :
: