Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
For each sinusoidal component of a signal, we need to determine its
frequency, amplitude, and phase (when needed). As a starting point,
consider the windowed complex sinusoid with complex amplitude
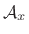 and frequency
and frequency 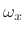 :
:
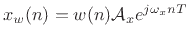 |
(11.20) |
As discussed in Chapter 5, the transform (DTFT) of this
windowed signal is the convolution of a frequency domain delta
function at 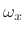 [
[
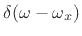 ], and the
transform of the window function,
], and the
transform of the window function, 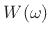 , resulting in a shifted
version of the window transform
, resulting in a shifted
version of the window transform
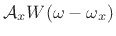 .
Assuming
.
Assuming 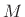 is odd, we can show this as follows:
is odd, we can show this as follows:
Hence,
At 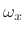 , we have
, we have
If we scale the window to have a dc gain of 1, then the peak magnitude
equals the amplitude of the sinusoid, i.e.,
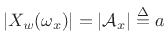 , as shown in Fig.10.8.
, as shown in Fig.10.8.
Figure:
Schematic diagram of a window
transform amplitude-scaled by 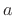 and frequency-shifted by
and frequency-shifted by 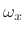 .
.
![\includegraphics[width=0.8\twidth]{eps/peak}](img1818.png) |
If we use a zero-phase (even) window, the phase at the peak equals the
phase of the sinusoid, i.e.,
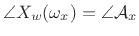 .
.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() and frequency
and frequency ![]() :
:
![\begin{eqnarray*}
X_w(\omega) &=& \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}[w(n)x(n)]e^{ -j\omega nT}
\qquad\hbox{(DTFT($x_w$))} \\
&=& \sum_{n=-(M-1)/2}^{(M-1)/2} \left[w(n){\cal A}_xe^{j\omega_xnT}\right]e^{ -j\omega nT}\\
&=& {\cal A}_x\sum_n w(n) e^{-j(\omega-\omega_x)nT} \\
&=& \zbox {{\cal A}_xW(\omega-\omega_x)}
\end{eqnarray*}](img1814.png)
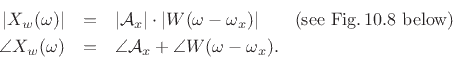
![]() , we have
, we have
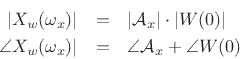
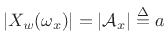 , as shown in Fig.10.8.
, as shown in Fig.10.8.
![]() .
.