Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Norm Properties
There are many other possible choices of norm. To qualify as a norm
on
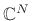 , a real-valued signal-function
, a real-valued signal-function
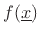 must
satisfy the following three properties:
must
satisfy the following three properties:
-
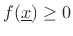 , with
, with
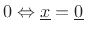
-
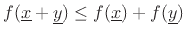
-
 ,
,
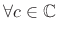
The first property, ``positivity,'' says the norm is nonnegative, and
only the zero vector has norm zero. The second property is
``subadditivity'' and is sometimes called the ``triangle inequality''
for reasons that can be seen by studying
Fig.5.6. The third property says the norm is
``absolutely homogeneous'' with respect to scalar multiplication. (The
scalar 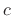 can be complex, in which case the angle of
can be complex, in which case the angle of 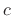 has no effect).
has no effect).
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() , a real-valued signal-function
, a real-valued signal-function
![]() must
satisfy the following three properties:
must
satisfy the following three properties: