 |
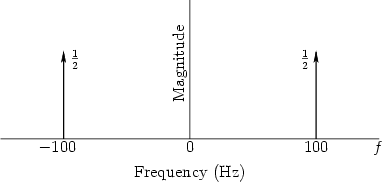
A sinusoid's frequency content may be graphed in the frequency domain as shown in Fig. 1.
 |
An example of a particular sinusoid graphed in Fig. 1 is given by
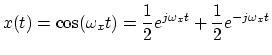
Figure 1 can be viewed as a graph of the magnitude
spectrum of ![]() , or its spectral magnitude representation
[4]. Note that the spectrum consists of two components
with amplitude
, or its spectral magnitude representation
[4]. Note that the spectrum consists of two components
with amplitude ![]() , one at frequency
, one at frequency ![]() Hz and the other at
frequency
Hz and the other at
frequency ![]() Hz.
Hz.
Phase is not shown in Fig. 1 at all. The phase of the components could be written simply as labels next to the magnitude arrows, or the magnitude arrows can be rotated ``into or out of the page'' by the appropriate phase angle as illustrated in [7, Fig. 4.8 on p. 43].