Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Consider the vector-difference example shown in
Fig.5.7.
The norm of the difference vector 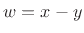 is
is
Figure 5.7:
Length of a difference vector.
![\includegraphics[scale=0.7]{eps/vecdist}](img756.png) |
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]