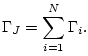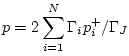Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
The delay-line inputs (outgoing traveling waves) are computed by
multiplying the delay-line outputs (incoming traveling waves) by the
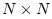 feedback matrix (scattering matrix)
feedback matrix (scattering matrix)
![$ \mathbf{A}= [a_{i,j}]$](img2084.png) . By
defining
. By
defining
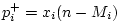 ,
,
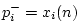 , we obtain the more
usual DWN notation
, we obtain the more
usual DWN notation
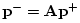 |
(G.103) |
where
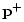 is the vector of incoming traveling-wave samples
arriving at the junction at time
is the vector of incoming traveling-wave samples
arriving at the junction at time 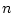 ,
,
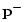 is the vector of
outgoing traveling-wave samples leaving the junction at time
is the vector of
outgoing traveling-wave samples leaving the junction at time 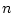 , and
, and
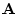 is the scattering matrix associated with the waveguide
junction.
is the scattering matrix associated with the waveguide
junction.
The junction of 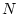 physical waveguides determines the structure of the
matrix
physical waveguides determines the structure of the
matrix
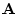 according to the basic principles of physics.
according to the basic principles of physics.
Considering the parallel junction of 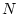 lossless acoustic tubes, each
having characteristic admittance
lossless acoustic tubes, each
having characteristic admittance
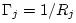 , the continuity of pressure and
conservation of volume velocity at the junction give us the following
scattering matrix for the pressure waves [409]:
, the continuity of pressure and
conservation of volume velocity at the junction give us the following
scattering matrix for the pressure waves [409]:
![$\displaystyle {\bf A} = \left[ \begin{array}{rrrr} \frac{2 \Gamma_{1}}{\Gamma_J...
...{2}}{\Gamma_J} & \dots & \frac{2 \Gamma_{N}}{\Gamma_J} -1\\ \end{array} \right]$](img2091.png) |
(G.104) |
where
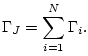 |
(G.105) |
Equation (G.105) can be derived by first writing the volume velocity at the
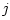 -th tube in terms of pressure waves as
-th tube in terms of pressure waves as
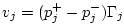 .
Applying the conservation of velocity we can find the expression
for the junction pressure. Finally, if we express the junction
pressure as the sum of incoming and outgoing pressure waves at any
branch, we derive (G.105). See §G.10 for further
details.
.
Applying the conservation of velocity we can find the expression
for the junction pressure. Finally, if we express the junction
pressure as the sum of incoming and outgoing pressure waves at any
branch, we derive (G.105). See §G.10 for further
details.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite and copy this work]
![]() feedback matrix (scattering matrix)
feedback matrix (scattering matrix)
![]() . By
defining
. By
defining
![]() ,
,
![]() , we obtain the more
usual DWN notation
, we obtain the more
usual DWN notation
![]() physical waveguides determines the structure of the
matrix
physical waveguides determines the structure of the
matrix
![]() according to the basic principles of physics.
according to the basic principles of physics.
![]() lossless acoustic tubes, each
having characteristic admittance
lossless acoustic tubes, each
having characteristic admittance
![]() , the continuity of pressure and
conservation of volume velocity at the junction give us the following
scattering matrix for the pressure waves [409]:
, the continuity of pressure and
conservation of volume velocity at the junction give us the following
scattering matrix for the pressure waves [409]: