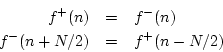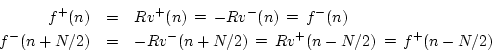
To find out how force waves recoil from a rigid termination, we may convert velocity waves to force waves by means of the Ohm's law relations of Eq. (4.6), and then use Eq. (4.10), and then Eq. (4.6) again:
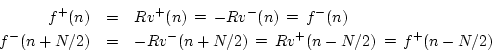
Thus, force waves reflect from a rigid termination with no sign inversion:5.1