Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Backward Euler Method
An example of an implicit method is the backward Euler method:
![$\displaystyle \underline{\hat{x}}(n) \isdefs \underline{\hat{x}}(n-1) + T\dot{\underline{\hat{x}}}(n) \eqsp \underline{\hat{x}}(n-1) + Tf[n,\underline{\hat{x}}(n),\underline{u}(n)] \protect$](img1710.png) |
(8.12) |
Because the derivative is now evaluated at time 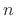 instead of
instead of 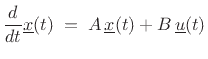 ,
the backward Euler method is implicit. Notice, however, that if time
were reversed, it would become explicit; in other words, backward
Euler is implicit in forward time and explicit in reverse time.
,
the backward Euler method is implicit. Notice, however, that if time
were reversed, it would become explicit; in other words, backward
Euler is implicit in forward time and explicit in reverse time.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![$\displaystyle \underline{\hat{x}}(n) \isdefs \underline{\hat{x}}(n-1) + T\dot{\underline{\hat{x}}}(n) \eqsp \underline{\hat{x}}(n-1) + Tf[n,\underline{\hat{x}}(n),\underline{u}(n)] \protect$](img1710.png)