Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Define the junction pressure 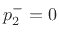 and junction velocity
and junction velocity 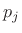 by
by
Then we can write
Note that
 , so we have found the velocity of the transmitted wave.
Since
, so we have found the velocity of the transmitted wave.
Since
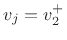 , the velocity of the reflected wave is simply
, the velocity of the reflected wave is simply
We have solved for the transmitted and reflected velocity waves
given the incident wave and the two impedances.
Using the Ohm's law relations, the pressure waves follow easily:
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() and junction velocity
and junction velocity ![]() by
by
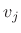
![\begin{eqnarray*}
p^+_1+p^-_1 &=& p^+_2\;=\;p_j\\ [10pt]
\,\,\Rightarrow\,\,R_1v^{+}_1 - R_1v^{-}_1 &=& R_2 v^{+}_2 \;=\; R_2 v_j\\ [10pt]
\,\,\Rightarrow\,\,R_1v^{+}_1 - R_1(v_j-v^{+}_1) &=& R_2 v_j\\ [10pt]
\,\,\Rightarrow\,\,2\,R_1v^{+}_1 - R_1 v_j &=& R_2 v_j
\end{eqnarray*}](img3534.png)
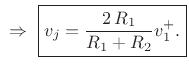
![$\displaystyle v^{-}_1 = v_j - v^{+}_1 = \left[\frac{2\,R_1}{R_1+R_2} - 1\right]v^{+}_1 = \frac{R_1-R_2}{R_1+R_2} v^{+}_1.
$](img3538.png)
![\begin{eqnarray*}
p^+_2 &=& R_2v^{+}_2 = R_2 v_j = \frac{2\,R_2}{R_1+R_2}p^+_1\\ [10pt]
p^-_1 &=& -R_1v^{-}_1 = \frac{R_2-R_1}{R_1+R_2} p^+_1
\end{eqnarray*}](img3539.png)