Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Geometric Series
Recall that for any complex number
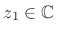 , the signal
, the signal
defines a geometric sequence, i.e., each
term is obtained by multiplying the previous term by the (complex) constant
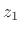 .
A geometric series is the sum of a geometric sequence:
.
A geometric series is the sum of a geometric sequence:
If 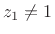 , the sum can be expressed in closed form:
, the sum can be expressed in closed form:
Proof: We have
When  ,
, 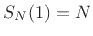 , by inspection of the definition of
, by inspection of the definition of
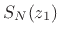 .
.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() , the signal
, the signal
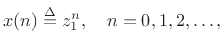
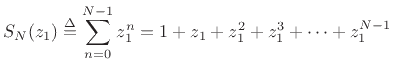
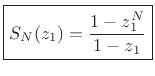
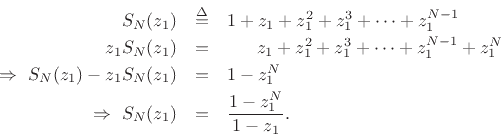
![]() ,
, ![]() , by inspection of the definition of
, by inspection of the definition of
![]() .
.