Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
For 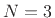 we have, in general,
we have, in general,
Let
Then
See §I.3.1 regarding computation of inner products in the matlab
programming language.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\underline{u}&=& [0,j,1] \\
\underline{v}&=& [1,j,j].
\end{eqnarray*}](img795.png)