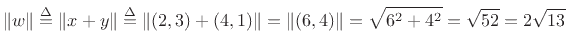Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Let's also look again at the vector-sum example, which is
redrawn in Fig.5.6. The norm of the vector sum 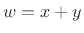 is
is
while the norms of 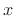 and
and 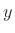 are
are 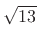 and
and 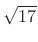 ,
respectively. We find that
,
respectively. We find that
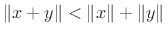 ,
which is an example of the triangle inequality. (Equality occurs
only when
,
which is an example of the triangle inequality. (Equality occurs
only when 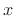 and
and 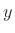 are collinear, as can be seen geometrically from
studying
Fig.5.6.)
are collinear, as can be seen geometrically from
studying
Fig.5.6.)
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]