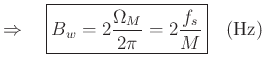Our ability to resolve two closely spaced sinusoids is determined by the main-lobe-width and sidelobe-level of our window's Fourier transform.
Let ![]() denote the main lobe width in Hz, with the main lobe width
defined as the width between zero crossings:
denote the main lobe width in Hz, with the main lobe width
defined as the width between zero crossings:

For the Rectangular Window (length ![]() ), we have
), we have
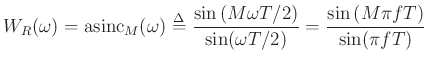
Main lobe width is ``two sidelobes wide''